Have you broken the habit of eating foods high in added sugar? Does this mean that you are not eating too much sugar?

First of all, congratulations, if you have broken this bad habit, you have taken a big step toward healthy eating. But, from the vegetables and fruits, we eat every day, rice noodles, corn, and potatoes, sugar is everywhere. However, the amount of sugar contained in different foods and the harm of different types of sugar to the human body are also different.
China has become the country with the heaviest diabetes burden in the world. Although diabetes does not mean that you eat too much sugar, diabetes does have an inseparable relationship with the amount of sugar you eat and the type of sugar you usually eat.
Today we will let you know, what is sugar? How to eat sugar, plus 15 subtle signs that you’re eating too much sugar.
What is sugar?

Sugar is the simplest form of carbohydrate, your body’s preferred form of energy, and is eventually broken down into glucose by the body. The body is inseparable from sugar, but too much sugar can put the body at risk of many diseases.
Generally, we divide sugar into natural sugar and added sugar. Natural sugars are carbohydrates found in various foods, such as sugars in fruits and vegetables, and sugars in starchy foods. Added sugar is sugar extracted from food, such as sucrose, maltose, etc. Generally, natural sugars are healthier than added sugars.
In addition, the content of natural sugars in different foods and the degree of influence on blood sugar are also different. For example, refined rice, noodles, and sugar in starchy foods can raise blood sugar quickly, so we generally recommend eating more whole grains. In addition, the sugar in fruits and vegetables will have much less impact on the body.
By choosing sugar in your food according to these two rules, you can take another step forward in eating healthily.
Risks of too much sugar

When you cut your finger, it becomes red and swollen. This is your body’s normal inflammatory response to repair itself. However, chronic inflammation is not healthy. Several studies have shown that diets high in sugar can increase blood sugar, free radicals, and compounds that increase inflammation. Make the inflammatory response longer and more intense.
Over time, too much sugar can increase your risk of obesity, increase your risk of diabetes, and possibly even increase your risk of chronic diseases such as certain cancers and heart disease.
Some studies also suggest that sugar may reduce the diversity of healthy bacteria in your gut in as little as a week, dulling your digestive system. At the same time, foods that are naturally rich in fiber (eg, fruits, and vegetables) have a positive effect on the contrary.
Seeing this, do you want to know how to tell if you are eating too much sugar? Here are 15 signs, and if you fit a few of them, then unfortunately I’m telling you, you’re probably consuming too much sugar.
- Lots of acne around your mouth and chin
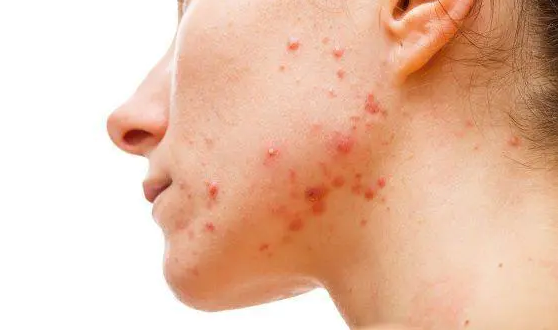
While experts say severe acne has nothing to do with the vast majority of people’s diet, some recent studies have linked acne to eating too many sugary foods. In theory, sugar increases hormone production and is linked to the inflammatory hormone acne. And this type of acne usually appears on the chin and around the mouth.
If you’re struggling with acne and don’t know-how, cutting back on added sugars in your diet may help.
- You are often moody

Some studies have linked sugar to mood disorders such as depression. In addition to blood sugar fluctuations, sugar can confuse neurotransmitters in the brain that regulate mood. Sugar, in particular, causes a spike in the feel-good hormone serotonin. Because we know carbs affect neurotransmitters, it may make you feel good at first. But the higher your blood sugar rises and the faster your blood sugar falls, the long run, they may make you feel worse. This is also why you often feel headaches and tiredness.
The best way to stabilize your blood sugar and mood is to eat more foods that take longer to digest, like whole grains, fiber, and protein.
- You have trouble falling asleep and sleep quality is poor

Eating too much sugary food before bed can make it harder to fall asleep, at least in the short term. When you try to relax, it boosts your energy by spiking your blood sugar, which can leave you jittery and energized instead. Shortly thereafter may have the opposite effect, as the sugar triggers the release of the neurotransmitter serotonin, making you feel relaxed and even sleepy. And even if you fall asleep, the sleep you get may not be satisfactory. Because your blood sugar drops dramatically during sleep.
So, stop eating as much as possible, especially sugary foods, four hours before bedtime so you can relax into sleep mode.
- Your skin wrinkles prematurely

A high-sugar diet has been shown to accelerate skin aging. This is because too much dietary sugar can react with proteins in the blood and form advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which destroy the structural proteins in skin collagen and elastin, impairing skin’s suppleness and elasticity. This makes your skin wrinkle faster and makes you look older. Restricting sugar intake can lead to significant improvements.
- You keep getting cavities

According to the Dental Association, sugar is the leading cause of tooth decay. When sugar settles on your teeth, it feeds on already naturally occurring plaque bacteria, and the acid produced can wear away tooth enamel (the hard surface of your teeth), leading to cavities. Worse yet is the combination of sugar and acid, commonly found in various beverages, that destroy tooth enamel. People who regularly drink these beverages tend to have more dental problems.
Solution: Swap out carbonated beverages that contain your favorite fruit tea or mineral water.
- You crave something sweet after every dinner

The more sugar you eat, the more likely you are to crave it. Sugar boosts your feel-good hormones. Because your brain feels good, it will want more again.
The habit of eating dessert after dinner can be one of the toughest eating traps. Habit can be as powerful as hunger when it comes to controlling food choices. If you have this bad habit, be sure to gradually improve it. This habit brings you no less harmful than smoking and drinking.
- You often feel hungry

If sugary foods are lacking in fiber or protein, it can be hard to fill you up. First of all, the body absorbs sugar very quickly, and the feeling of fullness is very poor. Second, sugar can cause your blood sugar to spike and drop quickly to low blood sugar, and it also releases a lot of ghrelin, so you feel hungry.
Do you have this feeling that eating rice, bread, etc. at the beginning of a meal will make you hungry more and more? But if you start with vegetable salads, lean meats, steaks, and other foods that contain fiber, healthy fats, and lean protein, you’ll be more likely to feel full.
- You have joint pain

Several studies have linked regular consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages with rheumatoid arthritis in women. Other studies have found that people who drink five or more sugar-sweetened beverages (including fruit juices) per week are more likely to develop arthritis. Of course, these studies have found only one link so far, which doesn’t necessarily mean that sugar causes arthritis directly.
- You have a hard time losing weight

While sugar itself doesn’t necessarily cause weight gain, the number of studies linking sugar and weight gain is undeniable. Eating sugar-rich foods regularly can cause you to consume too much energy.
Complex carbohydrates (like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables), healthy fats (like nuts and seeds), and lean proteins (like fish and chicken) can take your system longer to digest, keeping your blood sugar levels steady. If you eat a bar of chocolate at 4 pm, you’ll be hungry again soon. But if you eat an apple, you will feel very full.
- Difficulty concentrating and feeling confused

Your entire body, especially your brain, primarily uses carbohydrates (including sugar) as its main source of fuel. Therefore, when blood sugar drops rapidly after a high-sugar meal, it can lead to a lack of fuel in the brain. After that, your concentration and concentration continue to decline, which is why many people start to feel sluggish and sleepy in the afternoon, especially around 3 o’clock.
- Feeling that the fruit is not sweet enough

Eating sugar too often can alter how your taste buds respond to sweetness. When you taste fruit with family and friends, if everyone thinks that sweet fruit is not so delicious in your mouth, you must pay attention!
- You are often bloated

Salty foods are known to cause bloat, but foods high in sugar can also cause you bloating. Another thing to note is that if you are intolerant to the sugars fructose (the sugar in fruit) and lactose (dairy), you may also experience bloating and other symptoms in your belly.
- You feel a lack of strength while exercising

Sugar inhibits the body’s ability to synthesize protein into muscles. Once you start curbing your sweet cravings and limiting your sugar intake, you’ll start to see your workouts make a difference and feel stronger and stronger.
- Your blood pressure rises slightly
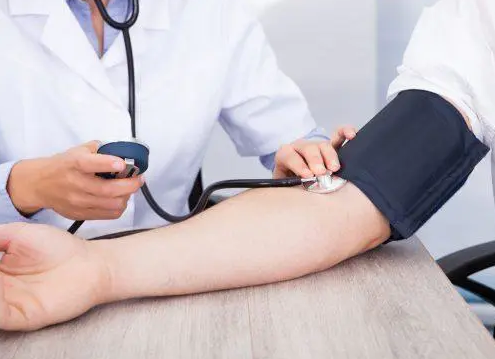
We all agree that excessive salt intake is an important cause of high blood pressure. According to one study, sugar has a worse effect on blood pressure than salt. Just a few weeks of a high-sucrose diet can dramatically increase systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Another study found that regular consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages increased the risk of high blood pressure by 8 percent.
- You become less physically active

It was said earlier that consuming too much added sugar can make you gain weight, and strangely it can also make you less physically active. In one study, two groups of mice were fed the same energy-standard diet. A group of mice that ate about 18 percent of the added sugar gained more body fat, even without consuming more calories. One reason was that the mice walked about 20 percent less in the small cages than mice that were not fed a sugar-sweetened diet.
How much sugar should you eat every day?
The Chinese Nutrition Society recommends that the daily added sugar should be limited to 25g per person. It is recommended to combine the thickness of the staple food and eat more vegetables, fruits, and milk at the same time. Although we should limit the intake of sugar, Kangzhou Health reminds you that the necessary carbohydrates are still necessary. We recommend a daily carbohydrate intake of 50-60% of total energy. Not sure how to calculate carbohydrate energy? Follow us, we will continue to popularize and enrich your health knowledge.
Count how many of the above 15 pits have you hit? Also share it with your friends and let them count.



